Effective Localization Strategies for Global SEO in Manufacturing
- SEO localization and global SEO work hand-in-hand to ensure a successful entry into new markets.
- Localization strategies include translating product information to align with local culture and buying contexts.
- SEO localization is a subset of global SEO, which means the former must work within the aspirations of the latter.
In this Article
Expanding operations into new global markets brings tremendous opportunities for revenue growth. However, actualizing this potential can be challenging. For instance, manufacturers must translate their websites and optimize content for local search engine visibility.
Without sufficient search visibility, manufacturers struggle to connect with local buyers. Even if a site offers excellent products and pricing, few local potential customers will find it. This leaves significant sales on the table.
The good news is that you can leverage global search engine optimization (SEO) and localization strategies to close the sales gap. These strategies enable industrial brands to boost discovery and drive more qualified traffic across borders. But what exactly does this entail? What crucial steps should you take when localizing sites for international search optimization?
This guide will discuss the crucial localization strategies for global SEO success. But first, you will learn what global SEO and localization are and why they matter in manufacturing.

Understanding Localization and Global SEO
Localization is the process of making something relevant to a particular place. In the manufacturing industry context, localization implies adapting products to the functional and cultural requirements of the target market.
So, what is SEO localization?
SEO localization is an aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) that involves optimizing digital content (blog posts, videos, product information, etc.) to enhance its visibility and relevance in specific target markets. This goes beyond traditional SEO practices by considering regional, linguistic, and cultural factors.
Why go to all this trouble? Aiming to satisfy the various factors outside of traditional SEO practices enables industrial marketers to achieve a crucial goal: to cater to the preferences of local audiences.
SEO localization ensures that your product information and other digital content rank high on search engine results pages (SERPs) in the specific regions where you seek to expand your business. It involves tailoring your SEO strategy to align with local search trends, language nuances, and user behavior.
Beyond visibility and relevance, SEO localization brings the following benefits:
- It drives more qualified organic traffic and discovery.
- It builds trust by using local dialects, categories, and semantics.
- It improves conversion rates through easily understood, translated content.
Localization happens in bits, which conglomerate into a robust strategy. Each bit, or component, deals with a specific aspect of the localization process. For instance:
- Keyword localization: It involves identifying and incorporating region-specific words or phrases that resonate with the local audience. This consists in understanding how buyers in the target region search for products and integrating those terms naturally into your content.
- Multilingual content: This component is about creating content in the languages spoken in the target markets. For example, if you are an American company looking to expand in Spain, the information on the product detail pages (PDPs) for the Spanish market should be in Spanish. It is appropriate to go a step further and incorporate the different dialects of the language. For instance, a PDP targeting buyers in North-East Spain should observe the Catalan linguistic and cultural uniqueness.
- Local link building: Building a strong backlink profile from reputable local websites enhances your site’s credibility to search engines and buyers. Localized link-building strategies involve collaborating with businesses, influencers, and organizations in the target region.
- Geotargeting: This approach to localization involves delivering customized content or experiences to users based on their geographical location. Geotargeting is a powerful tool that marketers use to enhance the relevance and effectiveness of product content in specific regions or markets. This includes displaying region-specific offers and pricing in local currencies.
Cultural sensitivity: Adapting your content to respect and incorporate cultural nuances is critical. Recall what we said about the Spanish market: it would be appropriate to consider cultural references, imagery, and themes that resonate positively with the Catalan audience when targeting Catalonia.

What is global SEO?
Global SEO describes the marketing strategies for optimizing content to improve international visibility, rankings, and traffic. Rather than targeting keywords and only optimizing for a single region, global SEO expands efforts for international opportunities. That is why it is also known as international SEO.
Unlike SEO localization, which targets individual regions, global SEO is the overarching strategy that guides digital content toward peak performance across diverse markets and search engines.
Think of it this way:
- SEO localization: Conquering individual peaks, adapting your approach to cater to each region’s unique terrain and challenges.
- Global SEO: Charting a comprehensive route across the mountain range ensures your brand resonates throughout the international landscape.
So, what exactly does global SEO entail?
- Understanding global search engine landscapes: Recognizing dominant search engines in different regions, like Baidu in China or Yandex in Russia, and adapting your technical strategy accordingly.
- Multilingual optimization: Creating high-quality content in the languages spoken by your target audiences, ensuring cultural relevancy and accessibility.
- Link building with a global lens: Forging partnerships and earning backlinks from websites relevant to your industry within each region. The goal is to boost your authority and trust across borders.
Mobile-first approach: If there is a unifying factor about internet access globally, it is that over 66% of global internet traffic comes from mobile phones. So, it makes sense to prioritize mobile optimization. This way, you have better odds of impacting the most significant number of buyers from across the globe. However, this approach should consider the fact that there are varying device preferences and internet speeds across different regions.

The intersection of localization and global SEO: An illustration
Consider a US-based power tools manufacturer looking to grow sales in Spain. This brand would leverage an integrated strategy encompassing thorough localization and optimization for the Spanish search market. But first, global SEO techniques will lay the groundwork.
In other words, global SEO is the foundation that provides a firm base for all localization efforts. Therefore, this brand’s Spanish odyssey is a segment of the overarching global SEO strategy.
Here is a possible global SEO strategy:
- Website structure: The website is optimized for multilingual content, with separate sections for each target market. Each section uses culturally relevant keywords and navigation menus.
- Mobile-first approach: The website is optimized for mobile devices, considering various internet speeds and device preferences across different regions.
- Backlink building: The brand builds backlinks from reputable websites in each target region, boosting its authority and trust in local search engines.
- Brand consistency: The brand maintains a consistent voice across all languages and regions while acknowledging cultural differences.
Now, let’s zoom in on the brand’s localization approach:
- Spanish content: They create high-quality product descriptions, blog posts, and landing pages in Spanish, addressing local needs and preferences.
- Keyword research: They identify relevant keywords Spaniards use when searching for power tools, incorporating them organically into their content.
- Cultural references: They use imagery and examples that resonate with Spanish audiences, building a connection and enhancing trust.
- Technical SEO tweaks: They adjust the website’s meta tags, URLs, and image alt text to comply with Spanish search engine preferences.
- Local partnerships: They partner with Spanish influencers and online retailers to reach their target audience more effectively.
This example illustrates the potent combination of global SEO and localization. The power tools manufacturer’s international SEO framework guarantees visibility, while the region-specific strategies optimize outcomes in each area.

Key Localization Strategies for Global SEO Success
1. Translating key pages into native languages
Your product information wouldn’t be helpful if it didn’t use the dominant language in the target region. So, localization starts with speaking the language of your target audience, both figuratively and literally.
For example, if a US-based manufacturer intends to expand into Spain, all local touchpoints must have Spanish as the default language. How can you go about implementing this tactic?
- Identify high-impact pages: Begin by identifying critical pages such as PDPs, service offerings, and landing pages. Typically, these are the pages that customers encounter first.
- Beyond literal translation, consider cultural nuances. Specific phrases or idioms may not have direct equivalents, so adapting the content to maintain cultural relevance is crucial. You might have to engage a native speaker to generate a new product copy.
Translate metadata and alt tags: As you adapt the content to buyers, also focus on search engine algorithms. For example, Google’s crawlers in Spain are designed to index Spanish-language content and meta elements. Therefore, translating metadata and alt tags ensures that search engines correctly index and display your pages in the relevant language.
2. Creating country or region-specific pages
When expanding operations internationally, the hallmark of sufficient SEO knowledge is understanding that a one-size-fits-all approach is insufficient. The knowledgeable marketer knows the new target market should have dedicated landing and product category pages.
So, suppose you are an American power tools brand setting up in Spain. You would:
- Build a dedicated Spanish landing page
- Focus copy and messaging explaining your brand’s value proposition to the Spanish construction sector.
- Create category pages showcasing your drills that Spanish contractors may prefer
- Optimize category page content around corresponding Spanish search queries
- Design Spanish-specific promotions and savings pages around annual events like Constitution Day (Día de la Constitución)
- Spotlight sales events focused on high-demand tools from Spanish builder surveys
Optimizing these types of localized, market-specific pages improves organic visibility and conversions. The focused content also enables extending search traffic through regional SERP features like localization packs.
3. Optimizing for local keywords or search intents
Localized SEO practices are part of a grander strategy, global SEO. As such, some may focus too much on the overarching goal at the expense of specific markets.
Your global website may be a magnificent palace, but visitors might get lost without a map. Local keyword research and search intent optimization are detailed maps of your operations. It guides potential customers straight to your doorstep in each target market.
Think of it like navigating a foreign city: you wouldn’t rely on a generic world map, would you? You’d grab a local map, understanding the specific street names, landmarks, and the local dialect to reach your destination efficiently. Similarly, local keyword research helps you know your target audience’s language when searching for your products.
So, if you are an American power tools manufacturer looking to exploit the revenue potential of the Spanish market, you would:
- Use keyword research tools (Semrush, Moz Keyword Explorer, Google Keyword Planner, etc.) to analyze high-volume Spanish search queries
- Uncover product-specific questions Spanish buyers are asking
- Extract keywords and questions with strong commercial intent, such as: “durable cobalt drill bits,” “industrial hammer replacement,” etc.
- Update Spanish product pages targeting the identified high-potential keywords
- Integrate keywords naturally within title tags, meta descriptions, and image names
- Craft informative content around questions Spanish buyers ask per keyword data
- Use FAQs, buyer guides, and comparison articles to answer Spanish information needs
- Iterate priority keywords across new localized content and product category pages
4. Adjusting content for cultural nuances
While languages differ from region to region, so do specific practices and notions among cultures. So, to truly conquer international markets, your content needs to shed its generic skin. It must blend seamlessly with each audience’s nuances.
What SEO practices can help your brand navigate this cultural landscape? Again, suppose you are an American brand expanding into Spain. Some specific tactics you can leverage include:
- Use photos of your tools being used in familiar applications, such as on construction sites
- Choose color palettes informed by colors that resonate best in Spanish culture. You can go a step further and zoom into specific regions, such as Andalusia, Basque Country, Catalonia, etc.
- Tailor messaging to reflect local communication styles and tonality preferences.
- Respect privacy expectations. For example, clearly display the use of do-not-track (DNT) cookie consent for European Union GDPR compliance. This also includes omitting any optional data capture that may seem intrusive by regional and country-specific standards.
This technique is beneficial in many ways beyond improving engagement and driving conversion. It sends positive signals to search engines, which improves rankings on SERPs.
However, remember that cultural adaptation is an ongoing process. So, stay informed about evolving trends, engage with local audiences, and constantly refine your approach to ensure your content remains culturally relevant and practical.
5. Enhancing on-page localization elements
So far, your SEO localization project is a masterpiece. It fits snuggly into the global SEO strategy and looks sufficient enough to guide your expansion efforts to success. However, one critical aspect is lacking: the finishing touches.
Enhancing on-page localization elements is the final brushstroke that transforms your website into a welcoming destination for target audiences.
Imagine entering a beautifully decorated home only to find mismatched cutlery and confusing instructions in a foreign language. On-page localization elements are the carefully placed silverware and clear, native-language labels that ensure every visitor’s smooth and satisfying experience.
Here’s how a manufacturing brand can make its website attractive to human buyers and search engine algorithms in the target market:
- Display product costs in the local currency. If the primary currency differs, dynamically update pricing to current conversion rates.
- Use in-country language call-to-action (CTA) buttons. For example, if you’re expanding into Spain and are an American company, replace English CTA with Spanish language equivalents –the “Comprar Ahora” button instead of “Buy Now.”
- Align the site language settings to the target market. For instance, set document language in HTML to “ES” to signal local targeting to Spanish search engine crawlers.
- If the product detail pages include priority shipping options, showcase the fastest or preferred local shipping choices at checkout. Also, provide estimated local delivery times to provide transparency.
- Stick to familiar address and date formats. Don’t confuse customers with foreign address formats – adapt online forms and checkout processes to accept local address conventions. Imagine a Spanish customer who can enter their postal code without having to decipher a different system. However, if the website uses the American date convention, this customer may find it hard to decipher when the order will arrive. The American date convention is middle endian, i.e., dates are traditionally written in the “month-day-year” order. On the contrary, like many other European countries, the date format follows the “day-month-year” order in Spain. Using convention-adhering formats for dates and addresses streamlines the purchase process and avoids low conversion rates.
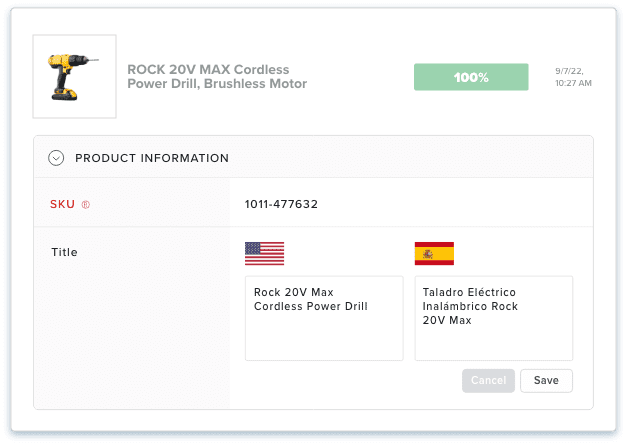
6. Managing localized product data with PIM and DAM
A common consequence of targeting multiple markets is fragmented product information. Suppose your American-based power tools brand manages Spanish translations and assets in local spreadsheets and folders. As you add more markets, translating and storing product data in individual market documents leads to the following:
- Inconsistent messaging and specifications for the same products
- Redundant and outdated translations across scattered Excel files
- Difficulty quickly updating details across all languages
- Teams unable to view translations side-by-side for accuracy checks
- Siloed assets like photos buried in hard-to-find folders
These inconsistencies and inaccuracies chip away at the trust and credibility the brand has worked so hard to earn. Finally, users begin complaining of poor experience, undermining your brand’s perception in the local market, a situation that can quickly spread to other markets.
Marketers often search the market for tools to streamline operations when they reach such a point. Tools like product information management (PIM Tool) and digital asset management software come to mind. They address the fragmentation challenges in the following ways:
A PIM Software like Catsy centralizes product information, creating a repository of all descriptions and technical specifications in one place. Furthermore, the tool provides side-by-side views of product details in different languages. Two crucial benefits arise from this functionality:
- First, the side-by-side views of different language product details enable easy cross-language validation. You do not have to hop from one spreadsheet to another to ensure all information is accurate.
- Secondly, the PIM allows you to simultaneously syndicate accurate and complete product information to all channels. For example, if your online storefronts across different markets are built on Shopify, Catsy product information management software supports simultaneous management of up to five stores. This means you can syndicate localized content to five different countries in a few short steps. This is far more productive than using spreadsheets.
Then, there are siloed digital assets. Scattered images, videos, and document files are the natural consequence of operating in different markets. For example, storing files for the US market in the same folder as the Spanish market makes little sense. These markets cannot be more different – a different language, currency, culture, etc.
In addition to PIM, you need a DAM system to store and organize the digital assets. Instead of engaging a different vendor for this tool, Catsy bundles PIM and DAM systems. This PIM and DAM integration implies the systems have prebuilt integrations that create a seamless working environment, which is impossible to achieve when using platforms from two different vendors.
Check also: PIM Buyer’s Guide
Besides housing images, manuals, and videos in a centralized database, a DAM can localize these assets by adding metatags and alt text. This enrichment, and readiness reporting on the PIM side, ensure that you have complete, accurate, and relevant product information.
The PIM SaaS / DAM collaboration effectively enhances operational efficiency and improves global SEO effectiveness. This centralized approach to product data management ensures consistency and accuracy, factors that search engines and buyers value the most.
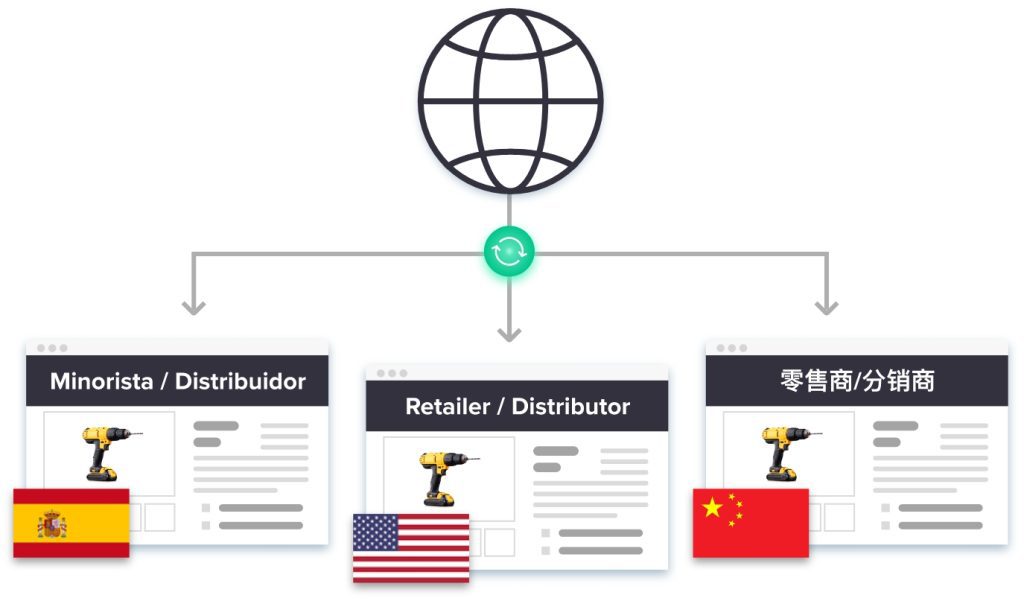
Key Takeaways
Expanding to international markets brings tremendous revenue growth opportunities for manufacturers. Yet achieving sales targets depends on connecting with local buyers in their languages and buying contexts.
So, as brands venture into new territories, it is imperative to design a robust localization strategy. This strategy should cater to the unique needs of each market while maintaining fidelity to the overarching SEO approach.
Beyond the meticulously designed and implemented localization and global SEO strategies, it is essential to consider the following:
- Testing the localization strategy: The journey doesn’t end with implementation; rigorous testing is crucial. Assessing the effectiveness of your localization strategy allows for adjustments and refinements based on real-world user interactions. The ongoing testing process ensures that the committed efforts align with the evolving demands of global markets.
- Building trust over time: Expanding into new markets demands patience – trust is not built overnight. The most important decision you can make is to commit to understanding local nuances, consistency, and authenticity. These are crucial elements in establishing enduring trust with diverse audiences.
While high-quality translation facilitates linguistic resonance, additional adaptations to imagery, messaging tone, and cultural nuances are equally crucial for connecting with foreign audiences. Effective localization aligns sites to local preferences.
Translation involves converting text from one language to another. On the contrary, localization is more extensive – it adapts sites and product information to region-specific cultural conventions, regulations, units of measure, terminologies, and expectations.
Yes. For example, Google runs hundreds of geotargeted domain versions using region-specific ranking algorithms and indexation rules. Sites must be optimized accordingly per target country to gain visibility for local searchers.
Product Information Management (PIM) and Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems streamline product data management across languages and regions. PIM ensures consistent, accurate product descriptions and specifications, while DAM organizes visual assets like images and documents efficiently. This helps deliver a seamless and localized product experience for every audience.
Building trust takes time and effort. Focus on understanding the customers’ needs, addressing region-specific concerns, and offering value-added services like local case studies, informative webinars, or even partnerships with trusted regional brands. Show them you’re invested in their success, not just making a quick sale.




